

DEPARTMENTS
BY THE NUMBERS
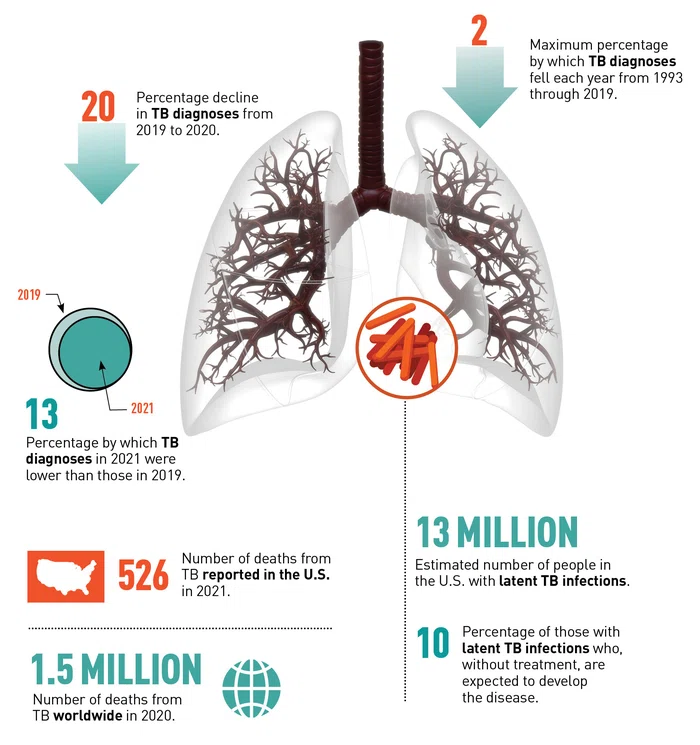
Tuberculosis in the United States
CDC announced in March that tuberculosis cases in the U.S. had fallen sharply since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic. The agency suggests the decline may be attributable to measures taken to control the spread of COVID-19, including physical distancing and mask wearing, as well as delayed or missed TB diagnoses due to the disruption of healthcare facilities caused by the pandemic. The similarity of symptoms of the two diseases may also have contributed to misdiagnoses, CDC said.
TB is a preventable, treatable bacterial disease spread through inhalation of infectious particles. Information about TB cases appears below.
TB is a preventable, treatable bacterial disease spread through inhalation of infectious particles. Information about TB cases appears below.
From “TB in the United States, 2021,” a CDC fact sheet:
“Health care and public health systems must be restored and strengthened to address TB disease in the wake of COVID-19. We must continue to ensure correct and timely diagnoses, focus on essential TB prevention and control activities, and expand services equitably to address persistent disparities in TB.”
Tap on the graphic to open a larger version in your browser.
SOURCES
CDC: “Effect of COVID-19 on Tuberculosis in the U.S.” (March 2022).
CDC: “TB in the United States, 2021” (PDF, 2022).
NIOSH: “Tuberculosis.”
World Health Organization: “Tuberculosis” (October 2021).