

DEPARTMENTS
BY THE NUMBERS
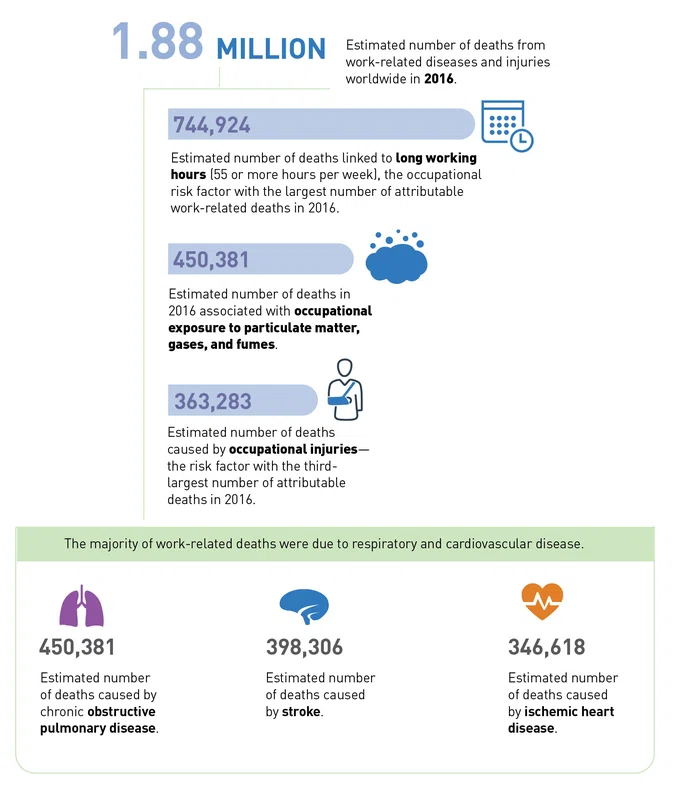
Leading Causes of Work-Related Deaths
Long working hours and workplace exposure to air pollution were the two occupational risk factors with the largest number of attributable work-related deaths in 2016, according to a joint report published in September by the World Health Organization and the International Labor Organization. The “joint estimates” report is the first of its kind and is intended to be used for the “global monitoring of exposure to occupational risk factors and work-related burden of disease and injury.” The report also examines the work-related burden of deaths associated with health outcomes. Information from the report appears below.
From “WHO/ILO Joint Estimates of the Work-Related Burden of Disease and Injury, 2000–2016: Global Monitoring Report”:
“For the effect of occupational risk factors on various health outcomes to be understood, quantification of the attributable burden of disease is vital. The WHO/ILO Joint Estimates will result in regular and harmonized, interagency monitoring of the work-related burden of disease, at the national, regional, and global levels.[...] However, burden of disease estimates should not be used in isolation for prioritization of action.”
SOURCE
World Health Organization and International Labor Organization: “WHO/ILO Joint Estimates of the Work-Related Burden of Disease and Injury, 2000–2016: Global Monitoring Report” (PDF, September 2021).
RELATED
The Synergist: “Long Working Hours, Heart Disease, and Stroke” (August 2021).
Tap on the graphic to open a larger version in your browser.