DEPARTMENTS
BY THE NUMBERS
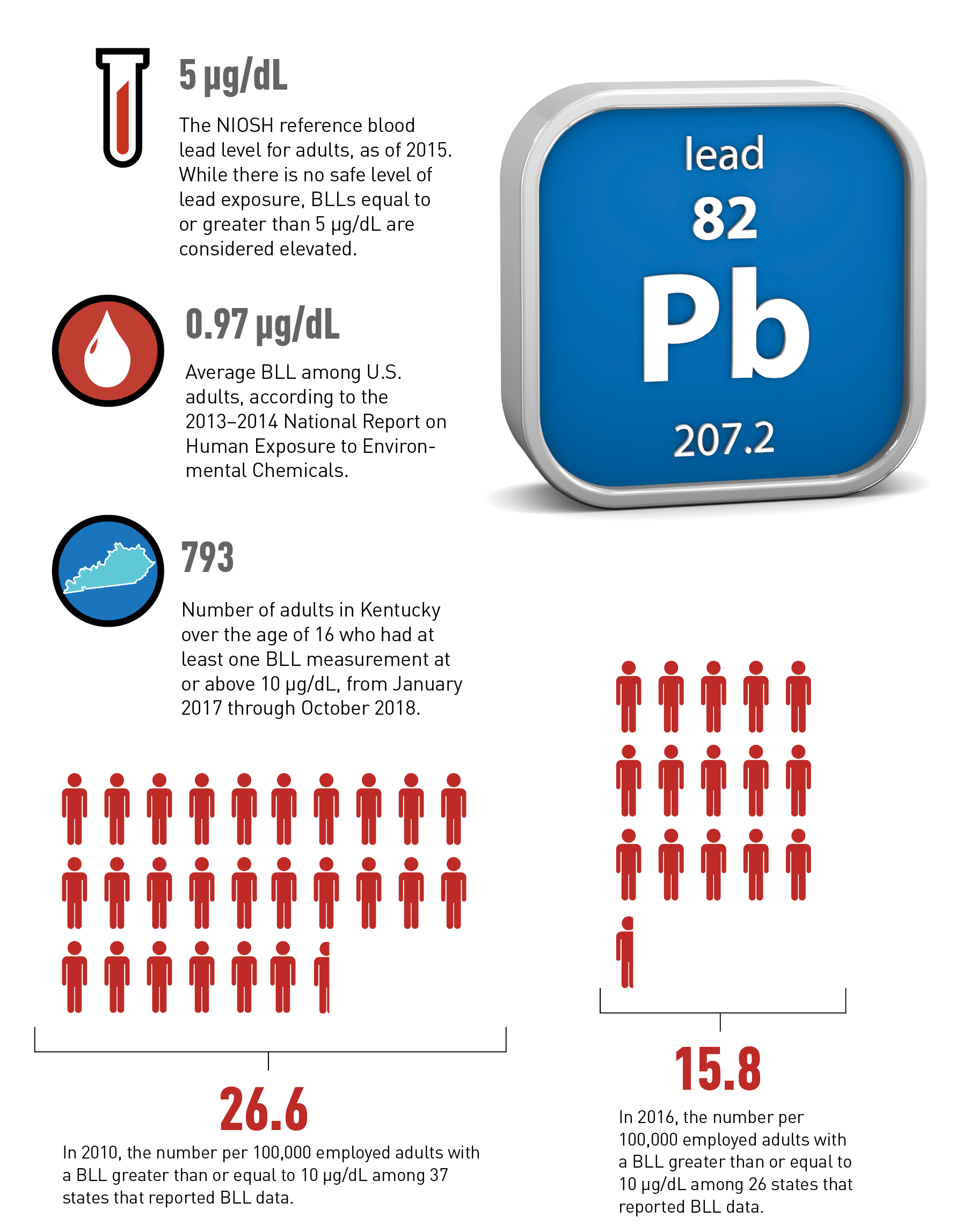
Blood Lead Levels in Kentucky Workers
A hazard alert issued in February by the Kentucky Injury Prevention and Research Center (KIPRC) drew attention to elevated blood lead levels among workers in the state. The hazard alert identified several industries that expose workers to lead, including auto repair, battery manufacturing, firing range instruction, plumbing and pipe fitting, mining, and welding. Data on blood lead levels in the United States are available through the NIOSH Adult Blood Lead Epidemiology and Surveillance program, or ABLES. Information from KIPRC and ABLES appears below.
From “Hazard Alert: Elevated Blood Lead Levels in Workers”:
“Since the National Institute for Occupational Safety & Health (NIOSH) began tracking BLL rates ≥10 µg/dL for adults in 2010, Kentucky has averaged rates 40% higher than the estimated national prevalence rate. There is no safe level of lead exposure.”
SOURCES
Kentucky Injury Prevention and Research Center: “Hazard Alert: Elevated Blood Lead Levels in Workers” (PDF, February 2020).
NIOSH: “Adult Blood Lead Epidemiology and Surveillance (ABLES): ABLES Data.”
NIOSH: “Adult Blood Lead Epidemiology and Surveillance (ABLES): Reference Blood Lead Levels (BLLs) for Adults in the U.S.”
Tap on the graphic to open a larger version in your browser.
In August, The Knoxville News Sentinel reported that a student intern and a researcher at Oak Ridge Associated Universities had devised an experiment to replicate the McCluskey incident in order to study the effects of radiation on the body. By irradiating vials of their own blood for different lengths of time, the researchers hope to generate data that clinicians and first responders can refer to following an exposure incident.
Read more from the News Sentinel.

